On this fourth note we will share progresses on the second suggested strategy, supply chain linkages.
On this fourth note related to commercialization strategies that add value and facilitate market access for agricultural producers, we will share progresses on the second suggested strategy, supply chain linkages.
The proposed definition of supply chain linkages is:
An articulation of formally or informally organized producers, who supply raw materials, fresh products, or products with little value added, that are marketed as generics to meet demand from agroindustrial firms, agroexporters, national or subnational government entities, and distribution chains (public or private), involve two or more intermediaries before reaching the consumer, and usually involve prior procurement and sales agreements (formal or informal).
These arrangements are driven by the actions of public initiative, in the case of state procurements, and private enterprise, in the form of agro-industrial firms or agro-exporters, distribution chains, supermarkets, and even large hotel and restaurant chains, or associations of same, as a result of their own initiatives in response to different interests (to ensure a supply of raw materials in the required amounts, quality, and timeliness; to minimize or distribute risk; to implement social responsibility practices;) or to implement public policy instruments that promote and facilitate these articulations. Social proximity is not a determinant in this type of arrangement and the economic distance is usually long.
Based in the analysis of multiple examples, in the following table you will find, a group of determinants and success factors.
Supply Chain Linkages, Determinants and Success factors table
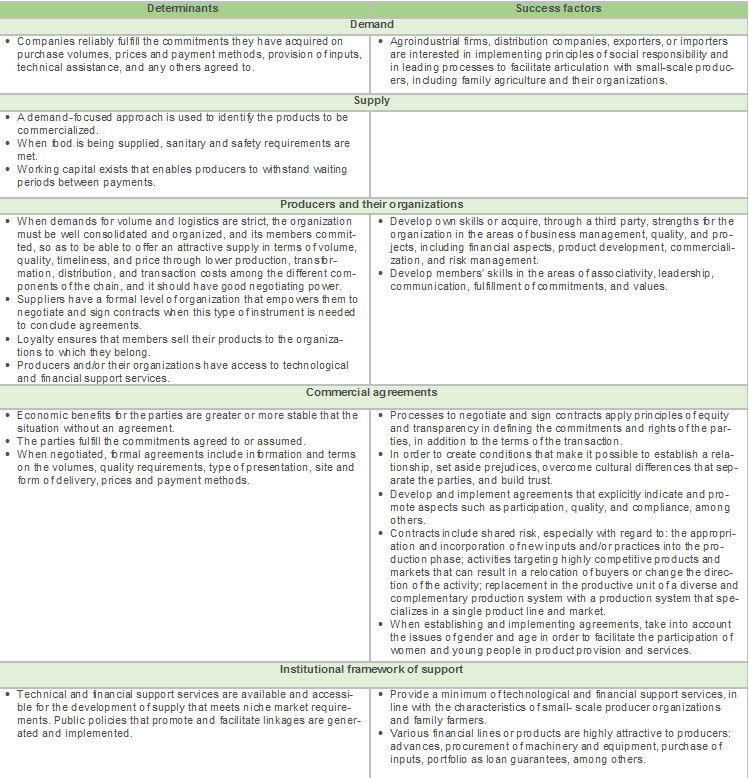
Supply chain linkages are a way to commercialize large volumes for organizations that have achieved a certain degree of development; they cannot be regarded as an alternative for all producers. Examples of this commercialization strategy are public food procurements, especially for school meal programs; production partnerships, supplier development or contract farming; provisioning of cooperatives by their members; inclusive businesses or businesses at the base of the pyramid; and social responsibility programs.
On the next bulletin we will address the last commercialization strategy: commercial linkages of differentiated products.
If you would like to review our previous notes related to this topic you can access them through the following link.
More information: daniel.rodriguez@iica.int
*This post appears in the IICA Delegation in the USA Newsletter – July – August 2016










