
In 2025, the international community will meet in Belém, Brazil—in the heart of the Amazon—for COP30, from 10 to 21 November.
The Home of Sustainable Agriculture of the Americas pavilion of the Inter-American Institute for Cooperation on Agriculture (IICA) at COP30 is a hemispheric meeting point for governments, international agencies, companies, academia, producers and rural communities. It showcases examples of concrete and inspiring solutions that foster innovation, resilience and social inclusion in agriculture and agrifood systems of the Americas.
For the fourth consecutive year, IICA will install the pavilion at COP, bringing together ministers, producers, scientists, international agencies and companies that are committed to building a more sustainable, competitive and inclusive agriculture sector.
Through panel discussions, dialogues and technical demonstrations, the Home of Sustainable Agriculture of the Americas (located in EMBRAPA’s AgriZone) will demonstrate how innovation, science and traditional knowledge can drive climate adaptation, mitigation and resilience.


Featured in the pavilion will be transformative initiatives in areas such as:
Presentation of an inventory of innovations applied to prevent and tackle forest fires and to assist in the recovery of affected areas, within the framework of the Agroforestry Firefighters of the Americas initiative.
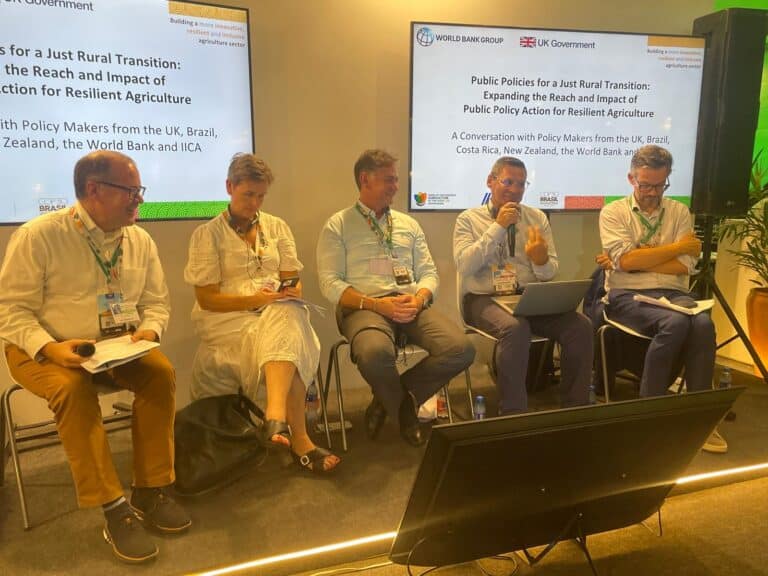

Belém do Pará, Brasil
November 27, 2025
Governments from Latin American countries met with the United Kingdom and international organizations at the pavilion of the Inter-American Institute for Cooperation on Agriculture (IICA) at COP30 to share experiences and perspectives on the public policies they are implementing to promote resilient agriculture and a just rural transition.
Tiempo de lectura: 3mins

Belém do Pará, Brasil
November 26, 2025
The ongoing transformation of agriculture in the Americas to consolidate its role as a guarantor of global food security and sustainability was showcased to the world by the Inter-American Institute for Cooperation on Agriculture (IICA) and its partners during COP30
Tiempo de lectura: 3mins
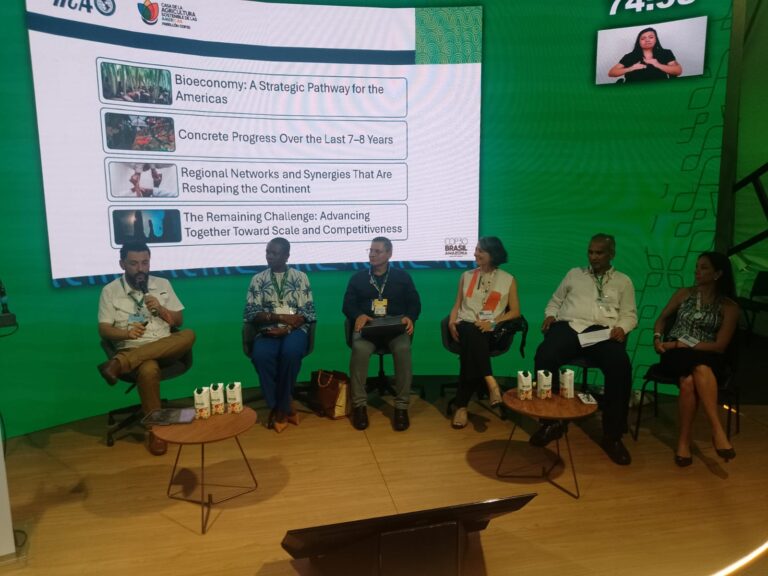

Belém do Pará, Brasil
November 24, 2025
Initiatives currently underway in the Amazon, the Andes, Mesoamerica, and the Caribbean attracted participants’ interest at the Home of Sustainable Agriculture of the Americas, the name of IICA’s pavilion, which was present for the fourth consecutive time at a COP, following the experiences in Egypt, the United Arab Emirates, and Azerbaijan.
Tiempo de lectura: 3mins




















The Conference of the Parties (COP) is the supreme decision-making body of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), the foremost international forum for climate policy negotiations.
Every year, the UNFCCC brings together its 197 State Parties and international agencies, the private sector, academia and civil society to assess progress in implementing agreements and define new collective goals in the face of the climate crisis.
During its sessions, the COP adopts decisions by way of consensus, reflecting the spirit of multilateralism and international cooperation that guides the Convention.
AOver the course of three decades, this process has led to important milestones such as the Kyoto Protocol (1997) and the Paris Agreement (2015), which laid the foundation for modern climate action.
In its thirtieth edition, COP30 will turn its gaze towards Brazil and the Amazon, making the event deeply symbolic. This year’s COP, which is expected to foster action and commitment, will focus on accelerating the implementation of the Paris Agreement and strengthening cooperation, funding, technology and climate adaptation mechanisms.



The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is an international treaty that guides global cooperation in the face of climate change. Adopted in 1992, the treaty entered into force in 1994, providing a legal and political framework aimed at stabilizing greenhouse gas concentrations at a level that would prevent dangerous interference with the climate system.
The Convention seeks to achieve this goal within a timeframe sufficient to allow ecosystems to adapt naturally to climate change, to ensure that food production is not threatened, and to guarantee sustainable economic development.
It currently has 197 State Parties, making it one of the most universal multilateral agreements in history.
In 2015, during COP21 in Paris, the countries adopted the Paris Agreement, a legally binding instrument that marked a new chapter in global climate governance.
The Agreement calls for maintaining the increase in the average global temperature well below 2ºC compared to pre-industrial levels, and for promoting additional efforts to limit this increase to 1.5ºC.
To achieve this goal, countries submit and periodically update their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), which reflect their commitment to emission reduction and adaptation.
The Agreement also fosters resilience, transparency and international cooperation through climate funding, technology transfer and capacity building.
Together, the UNFCCC and Paris Agreement provide a foundation for coordinated global efforts to address the climate crisis in an equitable, inclusive, and sustainable manner.

